Worksheet
Skeleton Code
Examples
Step 1: Flat Shading

Vertex Shader
void main()
{
gl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex;
}
Default computation for gl_Position
Fragment Shader
void main()
{
gl_FragColor=vec4(0.5,0.1,0.7,1);
}
Step 2: Position(Y)-based Shading
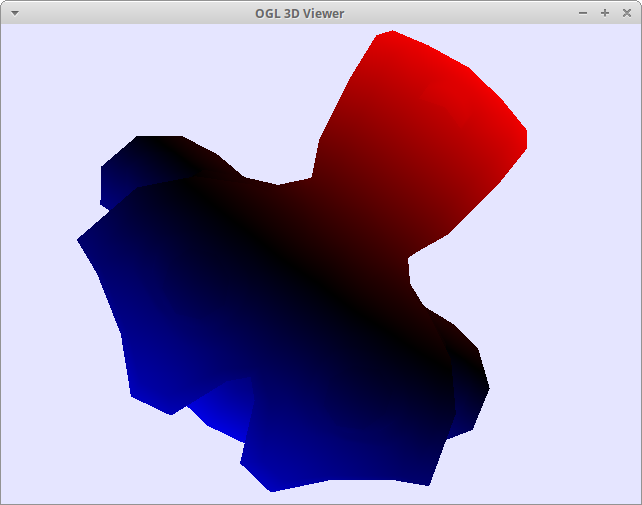
Color by model's position
Top of the monkey is always blue, regardless of the camera angle
*Use left-click on mouse to rotate the camera.
Vertex Shader
varying vec3 pos;
void main()
{
gl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex;
pos = gl_Vertex.xyz;
}
Fragment Shader
varying vec3 pos;
void main()
{
if(pos.y < 0)
gl_FragColor = vec4(1,0,0,1)*abs(pos.y);
else
gl_FragColor = vec4(0,0,1,1)*pos.y;
}
Step 3: View Position(Y)-based Shading
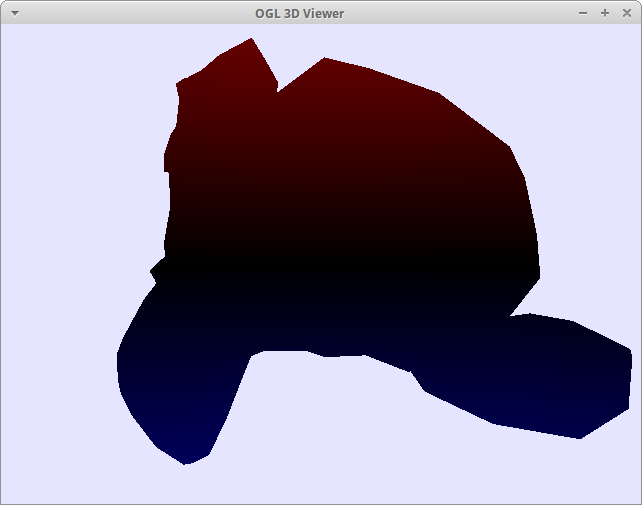
Color by fragment to eye vector (eye)
Top of the view is always red.
*Use left-click on mouse to rotate the camera.
Vertex Shader
varying vec3 pos;
void main()
{
gl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex;
pos= (gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex).xyz;
}
Fragment Shader
varying vec3 pos;
void main()
{
vec3 eye=normalize(-pos);
if(eye.y < 0.0)
gl_FragColor = vec4(1,0,0,1)*abs(eye.y);
else
gl_FragColor = vec4(0,0,1,1)*eye.y;
}
Step 4: Model Normal-based Shading
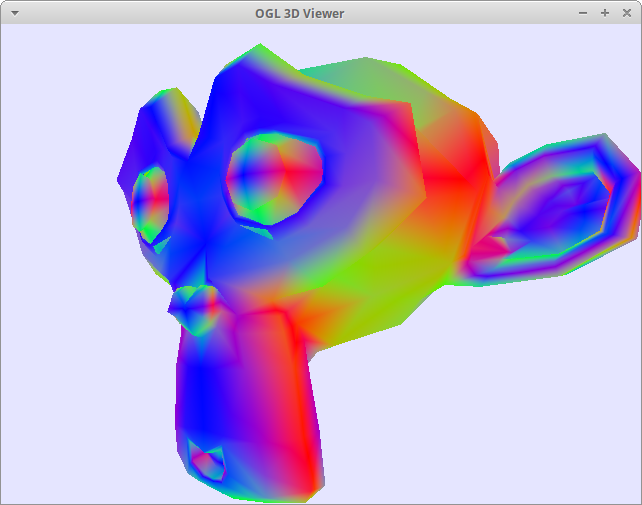
Color by normals of the monkey's surface
x: left/right of the monkey is red
y: top/bottom of the monkey is green
z: front/back of the monkey is blue
Regardless of the view
*Use left-click on mouse to rotate the camera.
Vertex Shader
varying vec3 normal;
void main()
{
normal = normalize(gl_Normal);
gl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex;
}
Fragment Shader
varying vec3 normal;
void main()
{
vec3 n = normalize(normal);
gl_FragColor=vec4(abs(n),1);
}
Step 5: View Normal-based Shading
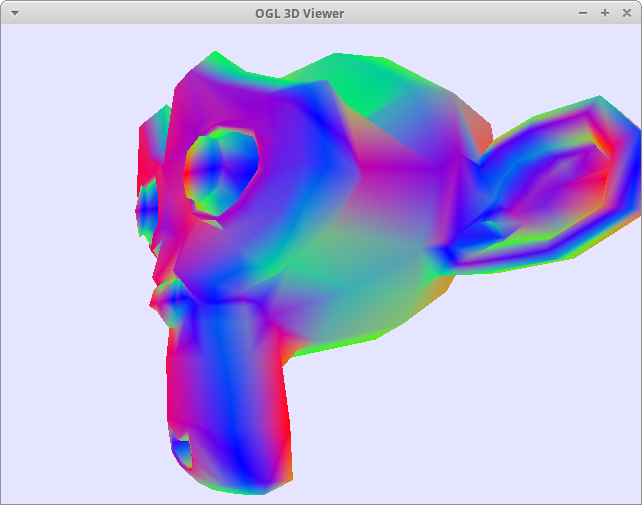
Color by normals of the monkey's surface rotated by the view
x: left/right of the view is red
y: top/bottom of the view is green
z: front/back of the view is blue
*Use left-click on mouse to rotate the camera.
Vertex Shader
varying vec3 normal;
void main()
{
normal = normalize(gl_NormalMatrix * gl_Normal);
gl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex;
}
Fragment Shader
//SAME AS PREVIOUS
varying vec3 normal;
void main()
{
vec3 n = normalize(normal);
gl_FragColor=vec4(abs(n),1);
}
Step 6: Light-direction-based Shading
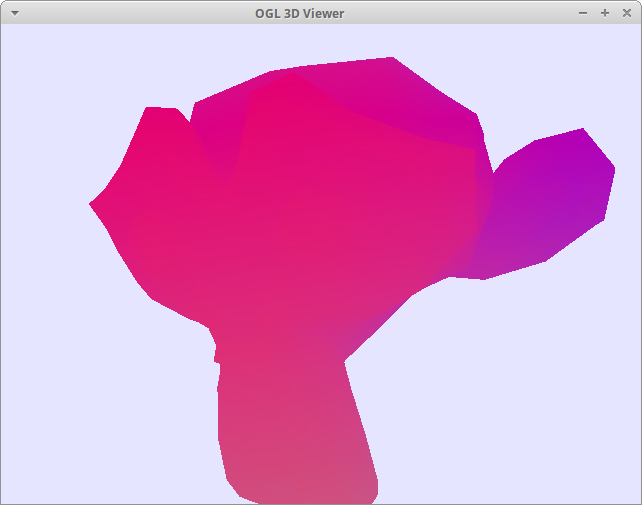
Color by the direction of light
Use left-click on mouse to rotate the camera.
Use right-click on mouse to rotate the light.
Vertex Shader
varying vec3 lightDir;
void main()
{
gl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex;
lightDir=normalize(gl_LightSource[0].position.xyz-pos);
}
Fragment Shader
varying vec3 lightDir;
void main()
{
vec3 l=normalize(lightDir);
gl_FragColor=vec4(abs(l),1);
}
FINAL: Phong Shading
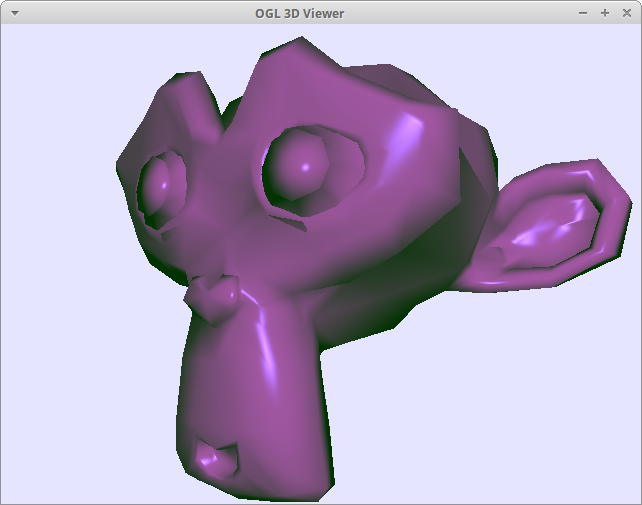
Phong Shading
Follow the comments and implement phong shading
Vertex Shader
varying vec3 lightDir,normal,pos;
void main()
{
//use example 3 to compute pos
pos=
//use example 5 to compute surface normal
normal=
//use example 6 to compute light_direction
lightDir=
//use example 1 to set gl_Position
gl_Position =
}
Fragment Shader
//HINTS:
// use gl_FrontMaterial's properties such as ambient, diffuse, specular
// and shininess for material properties. (use gl_LightSource for light
// specular contribution)
varying vec3 lightDir,normal,pos;
void main()
{
//use exaples above to set these vectors
//Don't forget to normalize
vec l,n,eye;
vec4 color;
// compute ambient component and add to color
// compute diffuse component and add to color
// compute specular component and add to color
gl_FragColor = color;
}